DiR(DiIC18(7))は、親油性の近赤外蛍光シアニン色素で、細胞膜の染色にご利用いただけます。他の細胞膜染色色素DiD、DiI、Neuro-DiO等と組み合わせて多重染色を行うことも可能です。
背景
DiR 色素について
DiR(DiIC18(7))は、細胞膜の染色に有用な親油性の近赤外蛍光シアニン色素です。18個の炭素からなる2本の炭素鎖が細胞膜に入り込むことで、別の細胞に色移りすることなく、特異的かつ安定的な染色が可能です。本色素は、エタノールでストック溶液を調製することができます。細胞は1〜10 uM濃度の色素と共に10〜20分インキュベートすることで染色されます。
| 名称 | DiR; DiIC18(7); 1,1′-dioctadecyl-3,3,3′,3′-tetramethylindotricarbocyanine iodide | 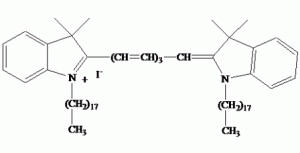 |
| λEx/λEm (MeOH) | 748/780 nm | |
| ε | 270,000 | |
| 形状/溶解性 | Dark blue-green oily solid soluble in ethanol, DMF or DMSO | |
| 分子量 | 1013.4 | |
| 化学式 | C63H101IN2 |
DiR
| 品名 | メーカー | 品番 | 包装 | 希望販売価格 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
DIR (DIIC18(7)) |
BTI | 60017-5MG | 5*1 MG |
¥39,000 |
DIR (DIIC18(7)) |
BTI | 60017-10MG | 10 MG |
¥58,000 |
[関連]細胞膜染色色素
| 品名 | メーカー | 品番 | 包装 | 希望販売価格 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
DID (DIIC18(5)) |
BTI | 60014-5MG | 5*1 MG |
¥29,000 |
DID (DIIC18(5)) |
BTI | 60014-10MG | 10 MG |
¥46,000 |
DII (DIIC18(3)) |
BTI | 60010 | 50 MG |
¥31,000 |
DiI in vegetable oil |
BTI | 60018 | 0.5 ML |
¥45,000 |
Neuro-DiO |
BTI | 60015 | 25 MG |
¥57,000 |
Neuro-DiO in vegetable oil |
BTI | 60019 | 0.2 ML |
¥62,000 |
製品使用文献多数!
- Biomaterials 34, 9171 (2013). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.08.039
- J Control Release (2013) http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2013.10.002
- Biomaterials (2013), http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.09.094
- Biomaterials (2013), http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.09.089
- International Journal of Nanomedicine 8, 2473–2485 (2013).
- Bioconjugate Chemistry (2013) doi: 10.1021/bc400055h
- International Journal of Pharmaceutics (2013), http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2013.05.015
- Pharm Res (2013) doi: 10.1007/s11095-013-1055-y
- Biomaterials (2013), http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.03.097
- International Journal of Nanomedicine 8, 1573–1593 (2013)
- International Journal of Nanomedicine 8, 1463–1476 (2013)
- Biomaterials (2013), http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.03.036
- Biomaterials (2013), http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.02.013
- Biomaterials (2013), http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.12.049
- Biomaterials (2012), http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.12.012
- Biomaterials (2013), http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.11.016
- International Journal of Nanomedicine 7, 163–175 (2012)
- J. Control. Release (2012) doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2011.12.017
- Pharm Res (2011) doi: 10.1007/s11095-011-0641-0
- Biomaterials (2011) doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.10.035
- International Journal of Pharmaceutics (2011) doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2011.09.008
- Molecular Pharmaceutics (2011) doi: 10.1021/mp200100f
- International Journal of Pharmaceutics (2011) doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2011.08.052
- International Journal of Pharmaceutics (2011) doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2011.07.021
- Molecular Pharmaceutics (2010) doi: 10.1021/mp100277h
- Journal of Controlled Release (2013), http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2013.10.026
- Biomaterials (2013), http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.09.062
- PLoS ONE (2013), doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0085003
- Int J Pharmaceut (2013), http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2013.12.016
- Journal of Drug Targeting (2014),http://informahealthcare.com/doi/abs/10.3109/1061186X.2013.851683
- ACS Nano (2014), doi: 10.1021/nn405155b
- Molecular Pharmaceutics (2014), doi: 10.1021/mp400751g
- Int J Pharmaceut (2014), http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2014.03.012
- Biomaterials (2014), http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.03.012
- Int J Pharmaceut (2014), http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2014.04.008
- Biomaterials (2014), http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.03.036
- Drug Delivery (2014), doi:10.3109/10717544.2014.903580
- Biomaterials (2014), http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.04.031
- Pharm Res. (2014), doi: 10.1007/s11095-014-1400-9
- Small (2014), doi: 10.1002/smll.201302786
- Biomaterials (2014), http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.04.117
- Biomaterials (2014), http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.06.022
- Mol. Pharmaceutics (2014), dx.doi.org/10.1021/mp500113p
- Vaccine (2014), http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2014.07.081
- Journal of controlled release (2014), http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.09.029
- Biomaterials (2014), http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.09.008
- International Journal of Nanomedicine 9, 5261–5271(2014).
- Journal of pharmaceutical sciences (2014), doi: 10.1002/jps.24291
- Biomaterials (2014), http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.11.044
- Int J Pharmaceut (2014), http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2014.12.039
- Acta Biomater (2015), http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2015.01.010
- Polym. Chem. (2015), doi: 10.1039/C4PY01422G
- Biointerfaces (2015), http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2015.02.041
- ONCOLOGY LETTERS (2015), doi: 10.3892/ol.2015.3242
- Acta Biomaterialia (2015), http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2015.05.021
- Drug Delivery (2015), http://informahealthcare.com/doi/abs/10.3109/10717544.2015.1040527
- Journal of Drug Targeting (2015), doi:10.3109/1061186X.2015.1058800
- Journal of drug targeting (2015), doi:10.3109/1061186X.2015.1064435
- Nanomedicine (2015), doi:10.2217/nnm.15.106
- Molecular Pharmaceutics (2015), doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.5b00222
- Bio-Medical Materials and Engineering 26 (2015), doi: 10.3233/BME-151384
- ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces (2015), doi: 10.1021/acsami.5b06043
- International Journal of Pharmaceutics (2015), doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2015.12.013
- RSC Advances (2015), doi: 10.1039/c5ra22233h
- Applied Materials Interfaces (2015), doi: 10.1021/acsami.5b09934
- Applied Materials & Interfaces (2016), doi: 10.1021/acsami.6b00036
商品は「研究用試薬」です。人や動物の医療用・臨床診断用・食品用としては使用しないように、十分ご注意ください。
※ 表示価格について
- 「DiR 親油性近赤外蛍光シアニン色素」は、下記のカテゴリーに属しています。

















 このページを印刷する
このページを印刷する








 中身を見る
中身を見る 中身を見る
中身を見る 中身を見る
中身を見る
 中身を見る
中身を見る