Solulink(ソルリンク)社のタンパク質−オリゴヌクレオチド結合キットは、簡単・効率的に2つのタンパク質とオリゴヌクレオチドを結合することができます。経験が少ない方、または、初めて行う方でも、必要に応じたタンパク質−オリゴヌクレオチドコンジュゲートを柔軟に作製することが可能です。キットには、必要なコンポーネント(S-HyNic および S-4FB を含む)全てと、長さ 100 bp までのオリゴヌクレオチドを簡単・特異的に架橋するためのプロトコールが含まれています。
触媒作用により簡単・効率的に結合 タンパク質‐オリゴヌクレオチド結合キット(Protein-Oligo Conjugation Kit)
- カテゴリから探す > 分子生物 > タンパク質の抽出/精製 > タンパク質の精製
背景
ソルリンク社のリンカー技術
ソルリンク社独自の、触媒作用によるヘテロ二官能性リンカー技術は、非常に簡単で高効率な手法です。作製したコンジュゲートは、UVによる追跡が可能で、安定した結合 (bis-arylhydrazone)を有し 、354 nm の吸光度で測定できます。
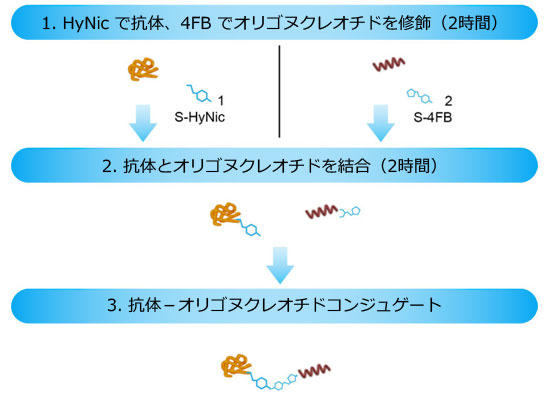
- S-HyNic (succinimidyl-6-hydrazino-nicotinamide) リンカーは、リジン残基またはN末端の第一級アミン (-NH2) を介して、タンパク質に結合します。
- S-4FB (succinimidyl-4-formylbenzamide) リンカーは、オリゴヌクレオチドに結合します。
- HyNic 修飾タンパク質を、4FB 修飾オリゴヌクレオチドと一緒にインキュベートすることで、触媒作用により結合します。
ソルリンク社のバイオコンジュゲーション法は、TurboLink™ 触媒を、オリゴヌクレオチドの4モル当量以上添加した場合、95% 以上のタンパク質がコンジュゲートに転換されます。変換率が高く、UVによる追跡が可能なことから、FPLC やダイアフィルトレーションなどのサイズ排除による精製法を用いて、過剰なオリゴヌクレオチドからコンジュゲートを簡単に精製・同定することができます。キットには反応2回分の試薬が含まれており、4時間以内の反応で、 40–60% のコンジュゲート(精製後)を得ることができます。作製したコンジュゲートは、イムノPCR、ハイブリダイゼーションなどに使用できます。
特長
- 触媒による結合−高効率・高収率
- 定量が可能−UV signature 波長・シンプルなUVスキャンを使用
- 安定性−他社のコンジュゲーションリンカーと比較して10倍以上安定
- 特異性−2種類のリンカーによりホモ共役を回避
構成内容
- S-HyNic
- S-4FB
- 10X 修飾バッファー
- 10X コンジュゲーションバッファー
- 10X TurboLink 触媒バッファー
- 7kDa 0.5 mL Zeba カラム
- 無水 DMF
- 0.5 mM 2-Hydrazinopyridine 試薬
- 0.5 mM 2-Sulfobenzaldehyde 試薬
- 7kDa 2.0 mL Zeba カラム
- 10X PBS
- 2.0 mL コレクションチューブ
- オリゴ再懸濁溶液
タンパク質−オリゴヌクレオチド結合キット
| 品名 | メーカー | 品番 | 包装 | 希望販売価格 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Protein-Oligo Conjugation Kit |
SLK | S-9011-1 | 1 KIT [2 conjugations] |
販売終了 |
【関連商品】
- タンパク質‐タンパク質結合キット
- 触媒作用により簡単・効率的に2つのタンパク質を結合するキット - オールインワン抗体標識キット(HRP/ALP/R-PE)
- 簡単!鮮やか!UV 測定によりリアルタイムに結合をトレース・定量できる!
参考文献
- Habtemichael EN, Brewer PD, Romenskaia I, Mastick CC. Kinetic evidence that Glut4 follows different endocytic pathways than the receptors for transferrin and alpha-2-macroglobulin. J Biol Chem 2011; 10.1074/jbc.M111.217935.
- Grotzky A, Manaka Y, Kojima T, Walde P. Preparation of Catalytically Active, Covalent α-Polylysine−Enzyme Conjugates via UV/Vis-Quantifiable Bis-aryl Hydrazone Bond Formation.Biomacromolecules. 2011:12(1):134-44. Epub 2010 Dec 20.
- Horikawa S, Bedi D, Li S, Shen W, Huang S, Chen I. Effects of Surface Functionalization on the Surface Phage Coverage and the Subsequent Performance of Phage-Immobilized Magnetoelastic Biosensors. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 2011;26(5):2361-7. Epub 2010 Oct 14.
- He J, Wang Y, Dou S, Liu X, Zhang S, Liu G, and Hnatowich D. Affinity Enhancement Pretargeting: Synthesis and Testing of a 99mTc-Labeled Bivalent MORF. 2010 Molecular Pharmaceutics Vol. 7, No. 4, 1118–1124.
- Shin IS, Maeng JS, Jang BS, You E, Cheng K, Li KCP, Wood B, Carrasquillo JA, Danthi SN, Paik CH.Tc-labeling of Peptidomimetic Antagonist to Selectively Target v 3 Receptor-Positive Tumor: Comparison of PDA and EDDA as co-Ligands. Current radiopharmaceuticals 2010;3(1):1.
- Kubler-Kielb J, Majadly F, Biesova Z, Mocca CP, Guo C, Nussenzweig R, Nussenzweig V, Mishra S, Wu Y, Miller LH. A bicomponent Plasmodium falciparum investigational vaccine composed of protein-peptide conjugates. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences2010;107(3):1172.
- Chawla K, Ham HO, Nguyen T, Messersmith PB. Molecular resurfacing of cartilage with proteoglycan 4. Acta Biomaterialia 2010;6(9):3388-3394.
- Iqbal M, Gleeson MA, Spaugh B, Tybor F, Gunn WG, Hochberg M, Baehr-Jones T, Bailey RC, Gunn LC. Label-Free Biosensor Arrays Based on Silicon Ring Resonators and High-Speed Optical Scanning Instrumentation. Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, IEEE Journal of2010;16(3):654-661.
- Ruggiero A, Villa CH, Holland JP. Imaging and treating tumor vasculature with targeted radiolabeled carbon nanotubes. International Journal of Nanomedicine 2010;5:783-802.
- D'Alessandria C, di Gialleonardo V, Chianelli M, Mather SJ, de Vries EF, Scopinaro F, Dierck RA, Signore A. Synthesis and Optimization of the Labeling Procedure of 99mTc-Hynic-Interleukin-2 for In vivo Imaging of Activated T lymphocytes. Mol Imaging Biol. 2010;12(5): 539–546.
- Liu G, Dou S, Chen X, Chen L, Liu X, Rusckowski M, Hnatowich DJ. Adding a clearing agent to pretargeting does not lower the tumor accumulation of the effector as predicted. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2010;25(6):757-62.
- Washburn AL, Gunn LC, Bailey RC. Label-free quantitation of a cancer biomarker in complex media using silicon photonic microring resonators. Analytical chemistry 2009;81(22):9499-9506.
- Johnson LM, Avens HJ, Hansen RR, Sewell HL, Bowman CN. Characterization of the Assaying Methods in Polymerization-Based Amplification of Surface Biomarkers. Australian Journal of Chemistry 2009;62(8):877-884.
- Hansen RR, Johnson LM, Bowman CN. Visual, base-specific detection of nucleic acid hybridization using polymerization-based amplification. Analytical biochemistry 2009;386(2):285-287.
- Myles W. Gardner MW and Brodbelt JS. Ultraviolet Photodissociation Mass Spectrometry of Bis-aryl Hydrazone Conjugated Peptides. Anal. Chem.2009,81,4864-4872.
- Liu G, Cheng D, Dou S, Chen X, Liang M, Pretorius PH, Rusckowski M, Hnatowich DJ. Replacing 99m Tc with 111In Improves MORF/cMORF Pretargeting by Reducing Intestinal Accumulation.Molecular Imaging and Biology 2009;11(5):303-307.
- Chen X, Dou S, Liu G, Liu X, Wang Y, Chen L, Rusckowski M, Hnatowich DJ. Synthesis and in Vitro Characterization of a Dendrimer- MORF Conjugate for Amplification Pretargeting.Bioconjugate chemistry 2008;19(8):1518-1525.
- Kattah MG, Coller J, Cheung RK, Oshidary N, Utz PJ. HIT: a versatile proteomics platform for multianalyte phenotyping of cytokines, intracellular proteins and surface molecules. Nature medicine 2008;14(11):1284-1289.
- Sharma S, Dominguez AL, Manrique SZ, Cavallo F, Sakaguchi S, Lustgarten J. Systemic Targeting of CpG-ODN to the Tumor Microenvironment with Anti–neu-CpG Hybrid Molecule and T Regulatory Cell Depletion Induces Memory Responses in BALB-neuT Tolerant Mice. Cancer research 2008;68(18):7530.
- Chaturvedi A, Dorward D, Pierce SK. The B cell receptor governs the subcellular location of Toll-like receptor 9 leading to hyperresponses to DNA-containing antigens. Immunity2008;28(6):799-809.
- Qi H, Cannons JL, Klauschen F, Schwartzberg PL, Germain RN. SAP-controlled T–B cell interactions underlie germinal centre formation. Nature 2008;455(7214):764-769.
- Liu G, Dou S, Rusckowski M, Hnatowich DJ. An experimental and theoretical evaluation of the influence of pretargeting antibody on the tumor accumulation of effector. Molecular cancer therapeutics 2008;7(5):1025.
- Liu G, Dou S, Pretorius PH, Liu X, Rusckowski M, Hnatowich DJ. Pretargeting CWR22 prostate tumor in mice with MORF-B72.3 antibody and radiolabeled cMORF. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2008 Feb;35(2):272-80.
- Walls ZF, Gambhir SS. BRET-based method for detection of specific RNA species. Bioconjugate chemistry 2008;19(1):178-184.
- Liu G, Dou S, He J, Liu X, Rusckowski M, Hnatowich DJ. Predicting the biodistribution of radiolabeled cMORF effector in MORF-pretargeted mice. European journal of nuclear medicine and molecular imaging 2007;34(2):237-246.
- Liu G, Dou S, Yin D, Squires S, Liu X, Wang Y, Rusckowski M, Hnatowich DJ. A novel pretargeting method for measuring antibody internalization in tumor cells. Cancer biotherapy & radiopharmaceuticals 2007;22(1):33-39.
- Buhl A, Metzger JH, Heegaard NHH, von Landenberg P, Fleck M, Luppa PB. Novel biosensor-based analytic device for the detection of anti-double-stranded DNA antibodies. Clinical chemistry 2007;53(2):334.
- Bailey RC, Kwong GA, Radu CG, Witte ON, Heath JR. DNA-encoded antibody libraries: a unified platform for multiplexed cell sorting and detection of genes and proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc2007;129(7):1959-1967.
- He J, Liu G, Dou S, Gupta S, Rusckowski M, Hnatowich D. An improved method for covalently conjugating morpholino oligomers to antitumor antibodies. Bioconjugate Chem2007;18(3):983-988.
商品は「研究用試薬」です。人や動物の医療用・臨床診断用・食品用としては使用しないように、十分ご注意ください。
※ 表示価格について
- 「タンパク質‐オリゴヌクレオチド結合キット(Protein-Oligo Conjugation Kit)」は、下記のカテゴリーに属しています。
-
- カテゴリから探す > 分子生物 > タンパク質の抽出/精製 > タンパク質の精製

















 このページを印刷する
このページを印刷する








 中身を見る
中身を見る 中身を見る
中身を見る 中身を見る
中身を見る
 中身を見る
中身を見る