SUPERFASLIGAND™ はFasリガンド(FasL/CD95/CD178)にN末端リンカーを結合したリコンビナントタンパク質です。通常のリコンビナントFasLよりも免疫反応を高活性化します。
背景
- 高い安定性
- 通常のFasLリコンビナントタンパクよりも、免疫反応を高活性化
- ネイティブのヒトFasLをグリコシル化をミミック
その他
- 由来:HEK 293細胞
ヒトFasL(APO-1L; CD95L; CD178)の細胞外ドメインのN末端にリンカーペプチド(26 aa)とFLAG®-tagを結合しています。 rhsSUPERFASLIGAND™ のグリコシル化はネイティブのFasLに近いです。 - 生理活性:ヒト、マウス、ラットのFas(CD95;APO-1)と結合します。Fas感受性細胞の細胞死を誘導します。(エンハンサーは不要です)
使用例
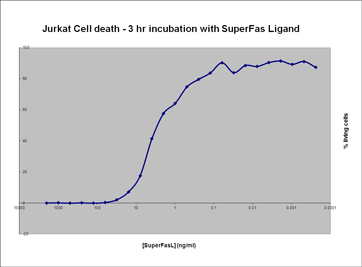
図1 Jurkat細胞を用いた細胞死
各濃度のSUPERFASLIGAND™ を加えたJurkat細胞(50,000cell/well)を3時間インキュベートし、細胞生存性を測定した。生存率%はSUPERFASLIGAND™ を含まないコントロールウェルと比較して決定した。
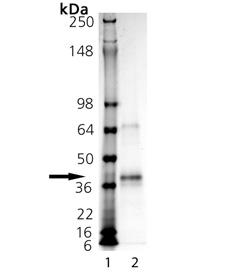
図2.Imperial stainにより染色したSDS-PAGE結果
レーン1分子量マーカー
レーン2:本商品(1μg)
SUPERFASLIGAND™:改良型FasL
| 品名 | メーカー | 品番 | 包装 | 希望販売価格 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
SUPERFASLIGAND Protein (soluble), Human |
ENZ | ALX-522-020-C005 | 5 UG [5_μg] |
¥77,000 |
SUPERFASLIGAND Protein (soluble), Human |
ENZ | ALX-522-020-3005 | 3*5 UG |
¥179,000 |
[関連商品]
使用文献多数!
- Lyapunov exponents and phase diagrams reveal multi-factorial control over TRAIL-induced apoptosis: B.B. Aldridge, et al.; Mol. Syst. Biol. 7, 553 (2014), Application(s): Death induction of HCT116, T47D and SKW6.4 cells, Abstract; Full Text
- FAIM-L Is an IAP-Binding Protein That Inhibits XIAP Ubiquitinylation and Protects from Fas-Induced Apoptosis: R.S. Moubarak, et al.; J. Neurosci. 33, 19262 (2013), Application(s): Death induction of rat neuronal Type II cells and murine cortical neurons, Abstract;
- Low FasL levels promote proliferation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells, higher levels inhibit their differentiation into adipocytes: M.R. Rippo, et al.; Cell Death Dis. 4, e594 (2013), Application(s): Induction of apoptosis or proliferation in human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell (BM–MSC) , Abstract;
- Nucleolin inhibits Fas ligand binding and suppresses Fas-mediated apoptosis in vivo via a surface nucleolin-Fas complex: J.F. Wise, et al.; Blood 121, 4729 (2013), Application(s): Apoptosis induction in Raji, Jurkat, and BC-3 cell lines, Abstract; Full Text
- Resistin-like molecule α stimulates proliferation of mesenchymal stem cells while maintaining their multipotency: I.A. Kolosova,et al.; Stem Cells Dev. 22, 239 (2013), Application(s): Apoptosis induction in mesenchymal stem cells, Abstract; Full Text
- Fas Ligand-Fas Signaling Participates in Light-Induced Apoptotic Death in Photoreceptor Cells: Q. Chang, et al.; Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 53, 3703 (2012), Application(s): Death induction of 661W cells, Abstract; Full Text
- Is Toso an antiapoptotic protein or an Fc receptor for IgM?: K. Honjo, et al.; Blood 119, 1789 (2012), Application(s): Death induction of Jurkat cells, Abstract; Full Text
- MS-275 sensitizes osteosarcoma cells to Fas ligand-induced cell death by increasing the localization of Fas in membrane lipid rafts: K. Rao-Bindal, et al.; Cell Death Dis. 3, e369 (2012), Application(s): Apoptosis induction in MS-275 sensitized osteosarcoma cells, Abstract; Full Text
- Antioxidant c-FLIP Inhibits Fas Ligand-Induced NF-κB Activation in a Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Akt-Dependent Manner: A.K. Iyer, et al.; J. Immunol. 187, 3256 (2011), Application(s): Death induction and NF-κB reporter gene assays with 293T and Jurkat cells, Abstract; Full Text
- Distinct TRAIL resistance mechanisms can be overcome by proteasome inhibition but not generally by synergizing agents: C. Menke, et al.; Cancer Res 71, 1883 (2011), Application(s): BJAB cells used in cell death assays with SuperFas Ligand , Abstract; Full Text
- TRAIL Receptor Signaling Regulation of Chemosensitivity In Vivo but Not In Vitro: C. Menke, et al.; PLoS One 6, e14527 (2011), Application(s): BJAB cells used in cell death assays with SuperFas Ligand , Abstract; Full Text
- A new function of the Fas-FasL pathway in macrophage activation: R. Chakour, et al.; J. Leukoc. Biol. 86, 81 (2009), Application(s): Death induction of bone marrow-derived macrophages and A20B lymphoma cells, Abstract; Full Text
- Fas Death Receptor Enhances Endocytic Membrane Traffic Converging into the Golgi Region: M. Degli Esposti, et al.; Mol. Biol. Cell 20, 600 (2009), Application(s): Studies on endocytosis and intracellular trafficking with Jurkat cells, Abstract; Full Text
- Regulation of Fas-mediated immune homeostasis by an activation-induced protein, Cyclon: S. Saint Fleur, et al.; Blood 114, 1355 (2009), Application(s): Death induction of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, Abstract; Full Text
- Fas-mediated killing of primary prostate cancer cells is increased by mitoxantrone and docetaxel: J.C. Symes, et al.; Mol. Cancer Ther. 7, 3018 (2008), Application(s): Death induction of primary prostate tumor cultures, Abstract; Full Text
- Resistance to FasL and tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-mediated apoptosis in Sézary syndrome T-cells associated with impaired death receptor and FLICE-inhibitory protein expression: E. Contassot, et al.; Blood 111, 4780 (2008), Application(s): Death induction of CTCL cell lines, SzS and HD cells, Abstract; Full Text
- The Fas Death Signaling Pathway Connecting Reactive Oxygen Species Generation and FLICE Inhibitory Protein Down-Regulation: L. Wang, et al.; J. Immunol. 180, 3072 (2008), Application(s): Death induction of AE2 and A549 cells, Abstract; Full Text
- A role of TRAIL in killing osteoblasts by myeloma cells: I. Tinhofer, et al.; FASEB J. 20, 759 (2006), Application(s): Death induction of primary osteoblasts, Abstract; Full Text
- Human Tumor-Released Microvesicles Promote the Differentiation of Myeloid Cells with Transforming Growth Factor-β-Mediated Suppressive Activity on T Lymphocytes: R. Valenti R., et al.; Cancer Res. 66, 9290 (2006), Application(s): Death induction of CD14+ monocytes and Jurkat cells, Abstract; Full Text
- Integrated mechanistic and data-driven modelling for multivariate analysis of signalling pathways: F. Hua, et al.; J. R. Soc. Interface 3, 515 (2006), Application(s): Caspase-8 and -3 cleavage kinetics in Jurkat cells, Abstract; Full Text
- Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Akt Positively Regulates Fas (CD95)-Mediated Apoptosis in Epidermal Cl41 Cells: B. Lu, et al.; J. Immunol. 176, 6785 (2006), Application(s): Death induction, PI3K/Akt phosphorylation assays, ELISA-based DNA fragmentation, ROS production and Fas promoter activity assays in Cl41 cells, Abstract; Full Text
- Effects of Bcl-2 Levels on Fas Signaling-Induced Caspase-3 Activation: Molecular Genetic Tests of Computational Model Predictions: F. Hua, et al.; J. Immunol. 175, 985 (2005), Application(s): Death induction of Jurkat cells, Abstract; Full Text
- Haploinsufficiency, rather than the effect of an excessive production of soluble CD95 (CD95ΔTM), is the basis for ALPS Ia in a family with duplicated 3' splice site AG in CD95 intron 5 on one allele: J. Roesler, et al.; Blood 106, 1652 (2005), Application(s): Death induction of Jurkat cells and normal activated peripheral T cells, Abstract; Full Text
- In vitro engagement of CD3 and CD28 corrects T cell defects in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: M. Bonyhadi, et al.; J. Immunol. 174, 2366 (2005), Abstract; Full Text
- Nitric Oxide Negatively Regulates Fas CD95-induced Apoptosis through Inhibition of Ubiquitin-Proteasome-mediated Degradation of FLICE Inhibitory Protein: P. Chanvorachote, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 280, 42044 (2005), Application(s): Death induction and analysis of regulation of Fas-induced apoptosis in BEAS-2B cells, Abstract; Full Text
- Fas Ligand Down-Regulates Cytokine-Induced Fas Receptor Expression on Insulinoma (NIT-1), But Not Islet Cells, from Autoimmune Nonobese Diabetic Mice: P. Augstein, et al.; Endocrinology 145, 2747 (2004), Abstract;
- Inhibition of metalloproteinase cleavage enhances the cytotoxicity of Fas ligand: P.G. Knox, et al.; J. Immunol. 170, 677 (2003), Abstract; Full Text
- NF-kappa B is required for surface Ig-induced Fas resistance in B cells: B.R. Schram & T.L. Rothstein; J. Immunol. 170, 3118 (2003), Abstract; Full Text
- Theileria parva-Transformed T Cells Show Enhanced Resistance to Fas/Fas Ligand-Induced Apoptosis : P. Küenzi, et al.; J. Immunol. 171, 1224 (2003), Application(s): Death induction of Theileria parva-infected TpM(803) T cells, Abstract; Full Text
- TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) frequently induces apoptosis in Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemia cells: K. Uno, et al.; Blood 101, 3658 (2003), Abstract;
- TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) frequently induces apoptosis in Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemia cells: K. Uno, et al.; Blood 101, 3658 (2003), Application(s): Death induction of 12 Ph1-positive leukemia cell lines, Abstract; Full Text
- Regulation of Fas (CD95)-induced apoptosis by nuclear factor-kappa B and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in macrophages: B. Lu, et al.; Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 283, C831 (2002), Application(s): Death induction of RAW 264.7 cells, Abstract; Full Text
- The Human Papillomavirus Type 16 E5 Protein Impairs TRAIL- and FasL-Mediated Apoptosis in HaCaT Cells by Different Mechanisms: K. Kabsch & A. Alonso; J. Virol. 76, 12162 (2002), Application(s): Death induction of HaCaT and A31 cells, Abstract; Full Text
- Tumor-cell resistance to death receptor-induced apoptosis through mutational inactivation of the proapoptotic Bcl-2 homolog Bax: H. LeBlanc, et al.; Nat. Med. 8, 274 (2002), Abstract;
- Fas ligand (CD95L) protects neurons against perforin-mediated T lymphocyte cytotoxicity: I. Medana, et al.; J. Immunol. 167, 674 (2001), Abstract; Full Text
- Fist/Hipk3: A FAS/Fadd-Interacting Serine/Threonine Kinase That Induces Fadd Phosphorylation and Inhibits FAS-Mediated Jun Nh2-Terminal Kinase Activation: V. Rochat-Steiner, et al.; J. Exp. Med. 192, 1165 (2000), Application(s): Death induction of Jurkat and JNK activation of 293T cells, Abstract; Full Text
商品は「研究用試薬」です。人や動物の医療用・臨床診断用・食品用としては使用しないように、十分ご注意ください。
※ 表示価格について
- 「SUPERFASLIGAND™ : 改良型FasL」は、下記のカテゴリーに属しています。

















 このページを印刷する
このページを印刷する








 中身を見る
中身を見る 中身を見る
中身を見る 中身を見る
中身を見る
 中身を見る
中身を見る