 商品紹介ページ QGel™ MT 3D Matrix
商品紹介ページ QGel™ MT 3D Matrix
QGel™ MT 3D Matrixは、そのまま使うことができる調製済みの凍結乾燥粉末です。
 商品紹介ページ QGel™ MT 3D Matrix
商品紹介ページ QGel™ MT 3D Matrix
QGel™ MT 3D Matrixは、そのまま使うことができる調製済みの凍結乾燥粉末です。
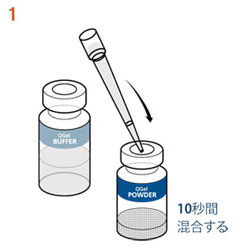
1. QGel™ MT 3D Matrix粉末にQGel™バッファーA400 µl を加え、約10秒間ボルテックスする。
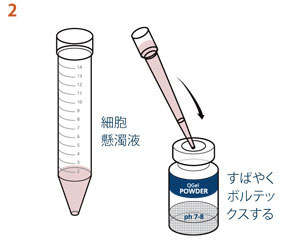
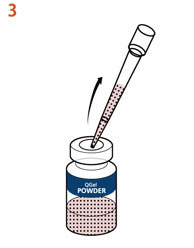
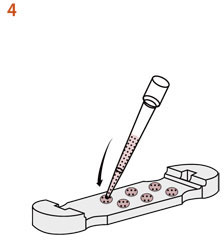
QGel™バッファーAを加えた後、ゲル化するまでの5〜10分間*4に、溶液を調製する事ができます。
ゲル化の反応速度はpHによって変わり、pHが高いほど速くなります。
*4 実験条件により変わります。
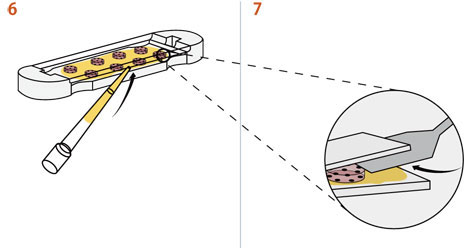
7. ゲルがディスク・キャスター表面へ、つかないように、スパチュラでディスクの端から少し持ち上げ、PBSを上、下の接触面を通して流れ込むようにします。
QGel™ 3D ディスク・キャスターはQGel™ディスク作製専用のキャスティング器具です。
この専用器具を使うことにより、安定性と再現性のあるゲル・ディスクが作製できます。
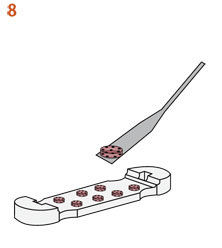
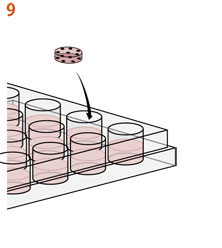

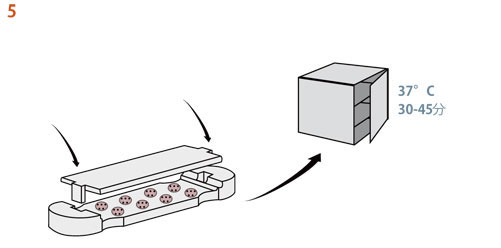
10. 出来上がったサンプルはすぐに長期培養に使用できます。
 QGel™ MT 3D Matrix 粉末とQGel™ バッファーAを混合したら、ゲルは5〜10分で硬くなります。ゲル化が始まると、ピペットの先端に糸状のものが付着し始めます(写真参照)。 その時から、ピペットでゲル溶液を取ることができなくなります。 ゲル・ディスクを作った後、ガラスのバイアルにゲル溶液が少し残っていますので、この残液を利用してゲル化の様子をモニターすることできます。 |
●幹細胞
Mouse Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Lei et al., DNA delivery from matrix metalloproteinase degradable poly(ethylene gylcol) hydrogels to mouse cloned mesenchymal stem cells, Biomaterials, 2009.
Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Adellow C et al., The effect of enzymatically degradable poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogels on smooth muscle cell phenotype,Biomaterials, 2008.
Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
Lee S et al., Engineering integrin signaling for promoting embryonic stem cell self-renewal in a precisely defined niche,Biomaterials, 2009.
●癌幹細胞
Mouse P19 Embryonal Carcinoma Stem Cells
Kraehenbuehl T et al., Three-dimensional extracellular matrix-directed cardioprogenitor differentiation: systematic modulation of a synthetic cell-responsive PEG-hydrogel, Biomaterials, 2008.
●癌細胞
Breast Cancer Cells
unbublished data yet, 2010, case courtesy of Dr. A. Casini and O. Zava (Prof. Dyson Lab), Institute of Chemical Sciences and Engineering, Swiss Institute of Technology (EPFL), Lausanne, Switzerland.
Ovarian Cancer Cells
unbublished data yet, 2010, case courtesy of Dr. Girieca Lorusso (Prof R
●線維芽細胞
Human Foreskin Fibroblasts
Raeber G, et al., Molecularly engineered PEG-hydrogels: a novel model system for proteolytically mediated cell migration,Biophysical Journal, 2005.
●軟骨細胞
Bovine Primary Chondrocytes
Park Y et al., Bovine primary chondrocyte culture in synthetic matrix metalloproteinase-sensitive poly(ethylene glycol)-based hydrogels as a scaffold for cartilage repair, Tissue Engineering, 2004.
●内皮細胞
Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells
Zisch A et al., Cell demanded release of VEGF from synthetic, biointeractive cell-ingrowth matrices for vasculararized tissue growth, The FASEB Journal, 2003.
【再生医療】
●Rat
Human Foreskin fibroblasts
Lutolf M et al., Synthetic matrix metalloproteinase-sensitive hydrogels for the conduction of tissue regeneration: engineered cell invasion characteristics, PNAS, 2003.
●Rat
Human foreskin fibroblasts
Lutolf M et al., Repair of bone defects using synthetic mimetics of collagenous extracellular matrices, Nature Biotechnology, 2003.
【in vivo 細胞送達】
●Rat
Human Foreskin fibroblasts
Lutolf M et al., Synthetic matrix metalloproteinase-sensitive hydrogels for the conduction of tissue regeneration: engineered cell invasion characteristics, PNAS, 2003.
●Rat
Human foreskin fibroblasts
Lutolf M et al., Repair of bone defects using synthetic mimetics of collagenous extracellular matrices, Nature Biotechnology, 2003.
商品は「研究用試薬」です。人や動物の医療用・臨床診断用・食品用としては
使用しないように、十分ご注意ください。
© COSMO BIO