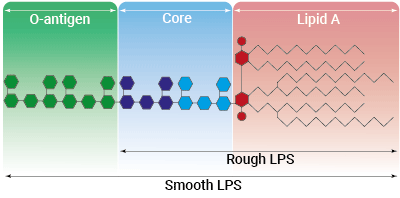
LPS-PG は、グラム陰性細菌 Porphyromonas gingivalis 由来のリポ多糖類 (LPS) のsemi-rough(sr) 型の製品です。 LPS-PG は歯周病のメカニズムにおける重要な毒性因子です。 LPS は、自然免疫系を活性化するグラム陰性細菌の主成分です。
LPSとTLR4の詳細はコチラ
作用機序
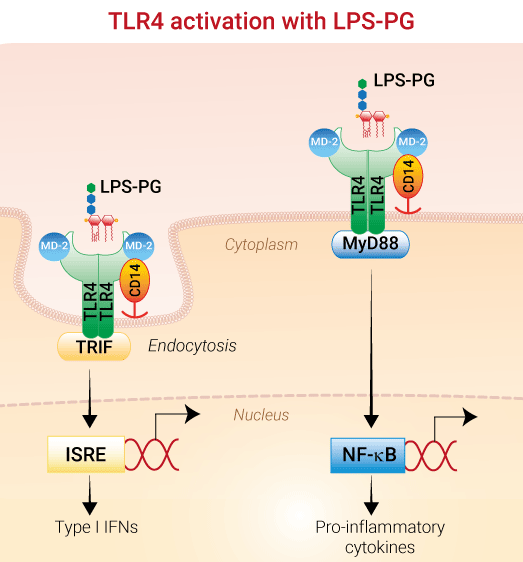
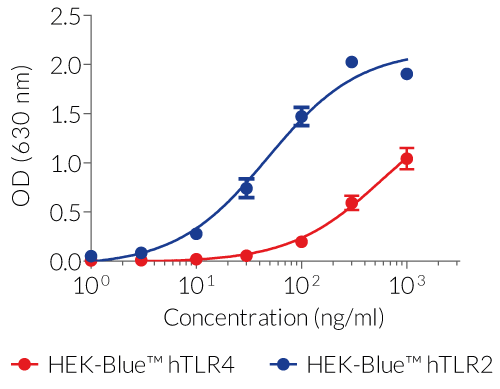
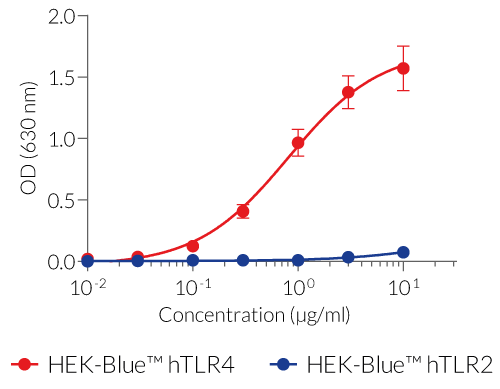
LPSの認識は主にTLR4によって媒介されます[1]。LPS-PGに対するTLR4の応答は、重要な補助分子であるCD14とMD2の存在に依存しています[2]。LPS-PG は、従来認識されている腸内細菌由来の LPS とは異なる、独特で複雑な化学構造をしています。LPS-PGがTLR4を欠損したC3H/HeJマウスで活性を示すという報告から、このLPSはTLR2リガンドであるという一般的な考えが生まれました[3, 4]。 しかし、LPS-PG の構造的および機能的研究により、TLR4 を介して細胞を活性化することが明らかになりました。LPS-PGのTLR2活性は、汚染されたリポタンパク質に起因すると考えられています[5]。
純度には二種類のグレードがあります。
- LPS-PG:標準的なリポ多糖類 (LPS) 製剤です。
- LPS-PG Ultrapure:リポタンパク質を除去する酵素で処理されているため、TLR4 のみが活性化されます。
- Poltorak A. et al., 1998. Defective LPS signaling in C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr mice: mutations in TLR4 gene. Science, 282:2085-8.
- Darveau R.P. et al., 2004. Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide contains multiple lipid A species that functionally interact with both toll-like receptors 2 and 4. Infect Immun. 72(9):5041-51.
- Kirikae T. et al., 1999. Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) of oral black-pigmented bacteria induce tumor necrosis factor production by LPS-refractory C3H/HeJ macrophages in a way different from that of Salmonella LPS. Infect Immun. 67(4):1736-42.
- Hirschfeld M. et al., 2001. Signaling by toll-like receptor 2 and 4 agonists results in differential gene expression in murine macrophages. Infect Immun. 69(3):1477-82.
- Ogawa T. et al., 2007. Chemical structure and immunobiological activity of Porphyromonas gingivalis lipid A. Front Biosci. 12:3795-812.

















 このページを印刷する
このページを印刷する