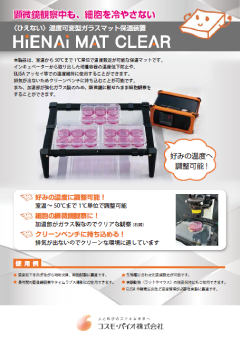
HyStem®技術は、チオール修飾ヒアルロン酸とチオール反応性架橋剤との反応に基づいており、in situでゲル化するハイドロゲルを生成し、細胞培養用足場や細胞または薬物送達媒体として使用することができます。HyStem®の主成分は、細胞外マトリックス(ECM)の主要構成要素の一つであるヒアルロン酸(HA)です。HAは最も単純なグリコサミノグリカン(負電荷、直鎖状の非硫酸化多糖類)であり、ECM内で圧縮強度、潤滑性、水和作用を提供します。また、細胞の接着や運動を制御、細胞の増殖や分化を仲介するなど、組織の構造的な構成要素だけでなく、活発なシグナル伝達分子でもあります。
【HyStem®製品ラインアップ】
| &nbs; |
HyStem® |
HyStem®-C |
HyStem®-HP |
| 特徴 |
|
- スターターキットとしておすすめ
- 接着タンパク質としてゼラチンを含有
|
- In vivoデリバリーにおすすめ
- ゲルに添加された成長因子がヘパリンとイオン結合し徐放される
|
- 30分程度で簡単に準備可能
- ネイティブ組織を模倣した基質
- In vitroでの3D培養及びIn vivoでのインジェクションが可能
|
| キット構成 |
- Glycosil® (Thiol-modified hyaluronic acid)
- Extralink®-Lite (PEGDA, polyethylene glycol diacrylate)
- Buffer A (Neutralization Solution)
- Buffer B (1X PBS, pH7.4)
|
- Glycosil® (Thiol-modified hyaluronic acid)
- Gelin-S® (Thiol-modified gelatin)
- Extralink® (PEGDA, polyethylene glycol diacrylate)
- Buffer A (Neutralization Solution)
- Buffer B (1X PBS, pH7.4)
|
- Heprasil® (thiol-modified hyaluronic acid and heparin)
- Gelin-S® (thiol-modified gelatin)
- Extralink® (PEGDA, polyethylene glycol diacrylate)
- Buffer A (Neutralization Solution)
- Buffer B (1X PBS, pH7.4)
|
| 使用確認済み細胞 |
| ヒト胚性幹細胞(ES細胞) |
骨髄由来間葉系幹細胞 |
| 臍帯血CD34+ 幹細胞 |
神経前駆細胞 |
| 肝幹細胞 |
膵島細胞 |
| 脂肪組織由来幹細胞 |
A549 肺がん細胞 |
| 心筋細胞 |
HUES-7 |
| 間葉系幹細胞 |
線維芽細胞 |


















 このページを印刷する
このページを印刷する