
NutriStem® hPSC XF 培地は、ヒトiPS/ES細胞培養用に最適化されたゼノフリー(Xeno-Free;XF)培地です。異種の動物由来成分を含まず、すべてヒト由来のタンパク質で構成されます。フィーダーフリー(Matrigel® コート) /オンフィーダー(MEF、HFF)のどちらの条件でも、未分化状態を維持した長期培養を可能にします。


NutriStem® hPSC XF 培地は、ヒトiPS/ES細胞培養用に最適化されたゼノフリー(Xeno-Free;XF)培地です。異種の動物由来成分を含まず、すべてヒト由来のタンパク質で構成されます。フィーダーフリー(Matrigel® コート) /オンフィーダー(MEF、HFF)のどちらの条件でも、未分化状態を維持した長期培養を可能にします。

NutriStem® hPSC XF 培地を用いてマトリゲル上でフィーダーフリー培養した幹細胞の形態写真
左:ヒト ES 細胞 H1 株
右:ヒト iPS 細胞 ACS-1014 株(63 歳白人男性のパーキンソン病患者皮膚由来iPS細胞)
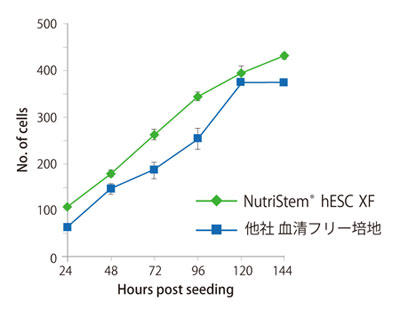
他社培地との性能比較
NutriStem® hPSC XF 培地または他社血清フリー培地で、96 well プレートに6 継代まで培養したヒトES 細胞H1 株を播種し、24 時間ごとに培地交換を行い、細胞数を測定した。NutriStem® hPSC XF 培地を使用して、他社培地と同等以上の細胞増殖が確認できた。
シングルセルクローニングが可能!! iMatrix-511 でも培養できます。
データご提供:近畿大学医学部附属病院 高度先端総合医療センター 再生医療部 竹原 俊幸 先生
NutriStem hPSC XF 培地(品番:05-100-1A)を使用して培養したヒト iPS 細胞(409B2 株)の形態写真
左:iMatrix-511 を使用したフィーダーフリー培養、中央:マトリゲルを使用したフィーダーフリー培養
右:マトリゲルを使用したシングルセル培養 (Y-27632 添加)
他社培地は増殖が良いのですが培養中の細胞死が多く、株によっては適さないものもありました。しかしながら Nutristem 培地は、細胞への影響に株差は少なく、生存率及び増殖能が高く維持されておりました。
また、完全に未分化状態を維持しているというよりは培養中に分化細胞が多少出現してくることから、自然に未分化維持が行えているような印象を持ちました。
さらに、シングルセルから増殖させることができるため、遺伝子導入を行った過剰発現株の作製だけでなく CRISPR/Cas9 システムを利用したゲノム編集など、遺伝子改変細胞株のシングルセルでの単離やその後の培養にも容易に行うことができました。
また、NutriStem 培地で培養した株は正常な核型を維持しておりました。
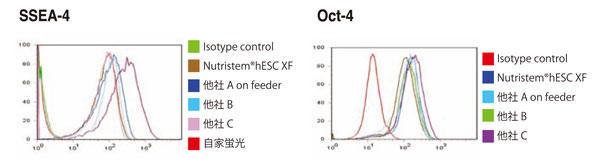
NutriStem® hPSC XF 培地または他社培地を用いてヒトES 細胞H1 株を6 継代まで培養し、フローサイトメトリーにてSSEA-4 と Oct-4 の発現を確認した。NutriStem® hPSC XF 培地にて培養した細胞において、両マーカーは90%以上の陽性を示した。
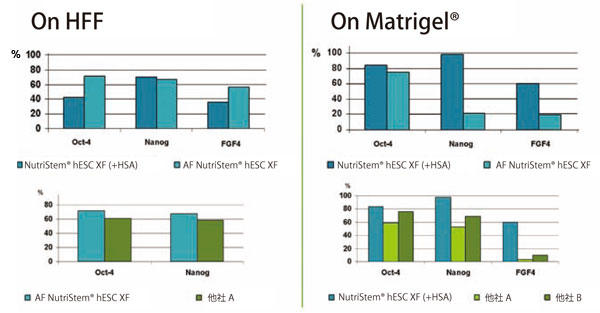
各々の培地にてES 細胞株H9.2 株を2 継代まで培養し、qPCR にてOct-4, Nanog, およびFGF-4 の発現を確認した。
オンフィーダー条件ではAF NutriStem® hPSC XF 培地で培養した条件が最も強い発現を示した(左)。
フィーダーフリー条件ではHSA を含むNutriStem® hPSC XF 培地で培養した条件が最も強い発現を示した(右)。
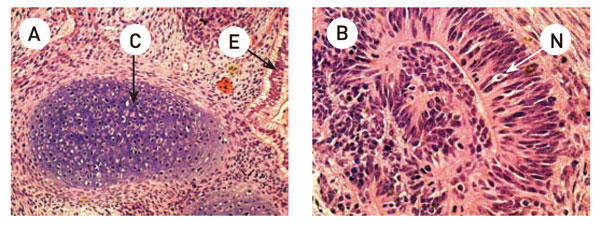
オンフィーダー条件、AF NutriStem® hPSC 培地で11 継代まで培養したヒトES 細胞H9.2 株をSCID-Beige マウスの後肢筋肉から注入し、テラトーマ形成試験を行なった。
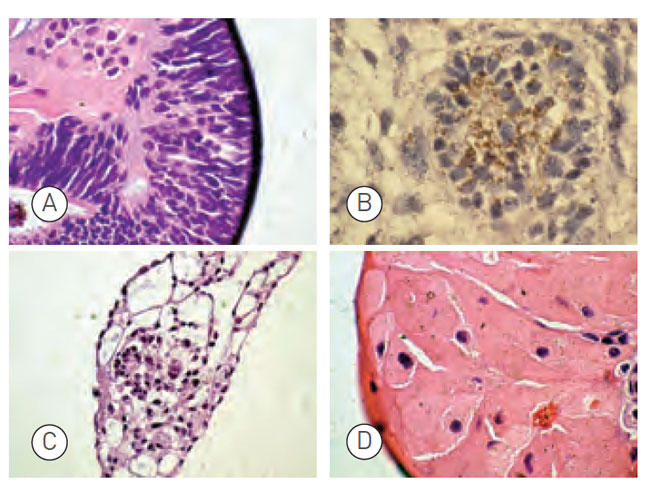
12 週間後、下記の三胚葉性の組織をH&E 染色組織切片から同定した。
(A) 軟骨(中胚葉:矢印C)、円柱上皮(内胚葉:矢印E)
(B) 神経ロゼット(外胚葉:矢印N)
ヒトES 細胞H9.2 株をMatrigel® コート条件、NutriStem® hPSC XF 培地で16 継代まで培養した後、胚様体形成試験を行なった。
血清含有培地にて14 日間浮遊培養した胚様体のH&E 染色組織切片から下記細胞タイプを同定した。
(A) 神経ロゼット(外胚葉)
(B) 神経ロゼットのチューブリン染色
(C) 原始血管(中胚葉)
(D) 巨核球(中胚葉)

iPS 細胞のシングルセルでの継代およびクローニングは、近年注目されている ゲノム編集技術 をiPS 細胞で使用する上で非常に有用となります。
NutriStem は、Laminin-521 をコートしたプレート上で、ROCK inhibitor を使用することなく高い生存率でのシングルセル継代が可能です。また、Laminin-521/ E-cadherin をコートしたプレート上では高効率なクローニングが可能となります。
注目文献:
1. S. Rodin et al ., Clonal culturing of human embryonic stem cells on laminin-521/E-cadherin matrix in defi ned and xeno-free environment. Nature Communications 5, 3195, 2014. [PMID : 24463987]
2. S. Rodin et al ., Monolayer culturing and cloning of human pluripotent stem cells on laminin-521–based matrices under xenofree and chemically defi ned conditions. Nature Protocols 9, 2354–2368 2014 [PMID : 25211513]
| 品名 | メーカー | 品番 | 包装 | 希望販売価格 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Nutristem(R) hPSC XF |
SSJ | 05-100-1A | 500 ML |
¥52,000 |
Nutristem(R) hPSC XF |
SSJ | 05-100-1B | 100 ML |
¥13,000 |
商品は「研究用試薬」です。人や動物の医療用・臨床診断用・食品用としては使用しないように、十分ご注意ください。
※ 表示価格について
© COSMO BIO